[SSS] OPTEE - Open Portable Trusted Execution Environment
OP-TEE는 ARM 기반의 비영리단체 Linaro에서 배포하는 TrustZone 기술이 적용된 TEE를 구현한 오픈소스를 의미한다.
TEE 개념처럼 Normal World / Secure World 두 개의 독립된 환경을 제공하고, ARM 아키텍처를 기반으로 둔다. 인텔 기반 X

각 World간 전환은 ARM 아키텍처에서 애플리케이션 계층 및 OS 계층보다 높은 권한 계층인 EL3에 구현되어 있는 Secure Monitor를 통해서 이루어진다.

OP-TEE 빌드하고 탭을 두개 띄우자. 하나는 Normal World 다른 하나는 Secure World

Normal World 탭에서 optee_example_hello_world 명령어가 잘 실행됨을 확인할 수 있음.
이제 이 예제를 복사해서 나만의 TEEencrypt를 만들어보자.
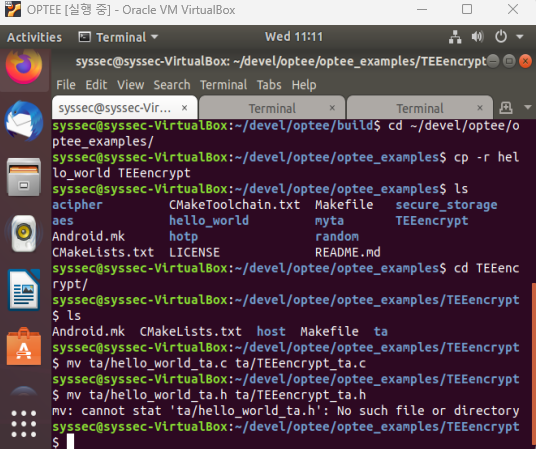

예제 디렉토리를 그대로 가져다가 활용하자.
이제 파일 구조가 제대로 잡혔고, UUID 생성과 헤더 수정 작업을 진행하자.
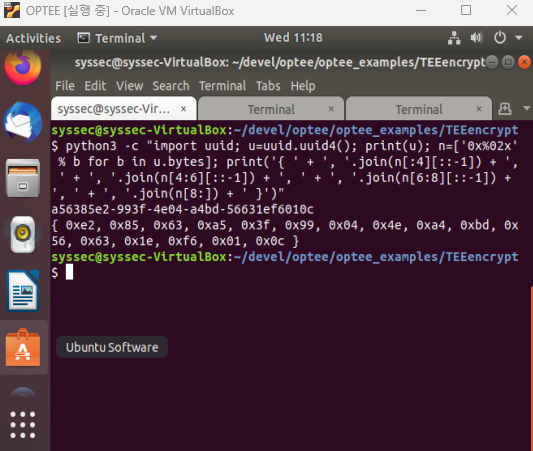

Trusted Application이 사용할 고유 ID를 만들고 TEEencrypt_ta.h 파일을 수정하자.

user_ta_header_defines.h 파일도 마찬가지로 수정해준다.
Client Application은 Normal World에서 실행되고, 사용자가 직접 조작하는 리모컨 역할을 수행한다.
Trusted Application은 Secure World에서 숨겨진 앱으로, 암호화 키를 가지고 작업을 수행한다.
지금까지 헤더 파일을 수정했는데, 이 작업은 TA에게 ID와 출입 자격을 만드는 과정이라고 생각하면 된다.
TEEencrypt_ta.h 파일은 CA와 TA의 약속을 정의한다.
이름을 hello_world에서 TEEencrypt로 바꿨고, UUID와 명령어 ID를 추가했다.
user_ta_header_defines.h 파일은 OP-TEE 시스템이 TA를 실행할 때 검사하는 파일이다.
TEEencryupt_ta.h 를 참조해서 UUID를 인식하도록 연결해준다.




이제 컴파일러에게 수정한 파일명과 UUID를 알려줘야 한다.
hello_world -> TEEencrypt / 구 UUID -> 신 UUID
모두 바꿔주고 다시 빌드해보자.
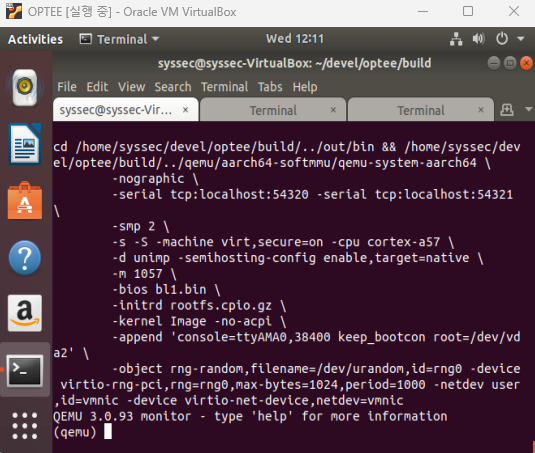
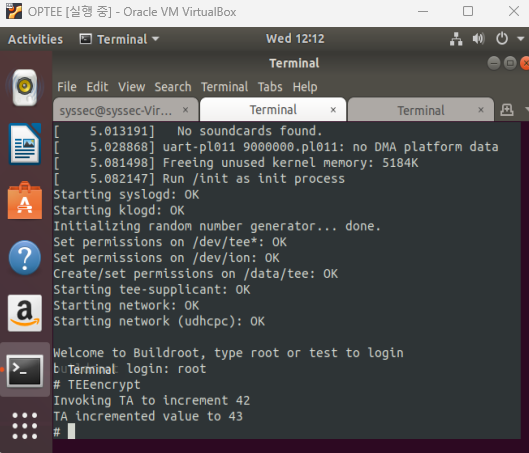
빌드 성공 후 TEEencrypt 명령어로 아까와 같은 메세지가 출력됨을 확인할 수 있다.
이제 기능 구현을 시작해보자. 단순히 숫자 42를 보내지 말고, 명령어와 텍스트 파일을 읽어서 TA에게 넘겨야 한다.
host/main.c 파일을 수정하자.
#include <err.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
/* OP-TEE TEE client API (built by optee_client) */
#include <tee_client_api.h>
#include <TEEencrypt_ta.h>
#define RSA_KEY_SIZE 1024
#define MAX_FILE_SIZE 1024
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
TEEC_Result res;
TEEC_Context ctx;
TEEC_Session sess;
TEEC_Operation op;
TEEC_UUID uuid = TA_TEEencrypt_UUID;
uint32_t err_origin;
char plaintext[64] = {0,};
char ciphertext[64] = {0,};
int len = 64;
if(argc != 3) {
printf("Usage: %s -e <filename>\n", argv[0]);
return 1;
}
res = TEEC_InitializeContext(NULL, &ctx);
if (res != TEEC_SUCCESS)
errx(1, "TEEC_InitializeContext failed with code 0x%x", res);
res = TEEC_OpenSession(&ctx, &sess, &uuid,
TEEC_LOGIN_PUBLIC, NULL, NULL, &err_origin);
if (res != TEEC_SUCCESS)
errx(1, "TEEC_Opensession failed with code 0x%x origin 0x%x",
res, err_origin);
if(strcmp(argv[1], "-e") == 0) {
printf("========================Encryption========================\n");
FILE *fp = fopen(argv[2], "r");
if(fp == NULL){
printf("File Open Error\n");
return 1;
}
fgets(plaintext, sizeof(plaintext), fp);
fclose(fp);
plaintext[strcspn(plaintext, "\n")] = 0;
len = strlen(plaintext);
printf("Plaintext : %s\n", plaintext);
memset(&op, 0, sizeof(op));
op.paramTypes = TEEC_PARAM_TYPES(TEEC_MEMREF_TEMP_INOUT, TEEC_VALUE_OUTPUT,
TEEC_NONE, TEEC_NONE);
op.params[0].tmpref.buffer = plaintext;
op.params[0].tmpref.size = len;
printf("Invoking TA to encrypt...\n");
res = TEEC_InvokeCommand(&sess, TA_TEEencrypt_CMD_ENC_VALUE, &op,
&err_origin);
if (res != TEEC_SUCCESS)
errx(1, "TEEC_InvokeCommand failed with code 0x%x origin 0x%x",
res, err_origin);
memcpy(ciphertext, op.params[0].tmpref.buffer, len);
printf("Ciphertext : %s\n", ciphertext);
FILE *fp_cipher = fopen("ciphertext.txt", "w");
fputs(ciphertext, fp_cipher);
fclose(fp_cipher);
FILE *fp_key = fopen("encryptedkey.txt", "w");
fprintf(fp_key, "%d", op.params[1].value.a);
fclose(fp_key);
printf("Encryption Complete! Check ciphertext.txt & encryptedkey.txt\n");
}
TEEC_CloseSession(&sess);
TEEC_FinalizeContext(&ctx);
return 0;
}
TEEC_Context - CA와 TEE간의 논리적인 연결을 담당한다.
TEEC_Session - CA와 TA간의 세션을 의미한다.
TEEC_Operation - TA에게 함수를 호출할 때 데이터를 주고받는 구조체를 선언함.
TEEC_UUID - 헤더 파일에서 설정한 UUID이다.
TEE 드라이버와 연결해서 Context를 생성하고, UUID와 Context를 사용해서 TEEencrypt TA와 연결한다.
TA에게 보낼 데이터의 타입과 내용을 정의한다. 파라미터를 2개 사용함.
TEEC_MEMREF_TEMP_INOUT - 공유 메모리 참조 관련 파라미터로, CA는 평문을 보내는 공간으로 사용하고, TA는 암호문으로 덮어써서 돌려줄 공간으로 사용한다.
TEEC_VALUE_OUTPUT - TA가 생성하고 암호화한 Random Key 값을 받을 때 사용한다.
TEEC_InvokeCommand 함수는 실제로 TA에게 작업을 요청하는 함수로, 함수가 실행되면 CPU가 Secure World로 넘어가서 enc_value 함수를 실행하고 돌아온다.
작업을 마치면 op.params[0].tmpref.buffer 에는 암호문이, op.params[1].value.a 에는 암호화된 키가 들어있다.
두 값을 ciphertext.txt 와 encryptedkey.txt로 분리해서 저장한 후 세션을 닫는다.
핵심은...
Normal World에서 작동해서 파일 시스템 접근이 불가능한 TA 대신 파일을 읽고 쓰는 역할을 수행한다.
암호화 연산과 키 생성 코드는 TEEC_InvokeCommand 함수를 통해 Secure World 에서 처리하는게 포인트.

main.c 를 수정했으니 다시 빌드하고 제대로 됐는지 확인해보자.
Plaintext : 13months 가 출력된걸 보니 파라미터 준비까지는 제대로 한 듯..
이제 Secure World 부분 코드를 수정해보자.
#include <tee_internal_api.h>
#include <tee_internal_api_extensions.h>
#include <TEEencrypt_ta.h>
#define ROOT_KEY 3
/*
* Called when the instance of the TA is created. This is the first call in
* the TA.
*/
TEE_Result TA_CreateEntryPoint(void)
{
DMSG("has been called");
return TEE_SUCCESS;
}
/*
* Called when the instance of the TA is destroyed if the TA has not
* crashed or panicked. This is the last call in the TA.
*/
void TA_DestroyEntryPoint(void)
{
DMSG("has been called");
}
/*
* Called when a new session is opened to the TA. *sess_ctx can be updated
* with a value to be able to identify this session in subsequent calls to the
* TA. In this function you will normally do the global initialization for the
* TA.
*/
TEE_Result TA_OpenSessionEntryPoint(uint32_t param_types,
TEE_Param __maybe_unused params[4],
void __maybe_unused **sess_ctx)
{
uint32_t exp_param_types = TEE_PARAM_TYPES(TEE_PARAM_TYPE_NONE,
TEE_PARAM_TYPE_NONE,
TEE_PARAM_TYPE_NONE,
TEE_PARAM_TYPE_NONE);
DMSG("has been called");
if (param_types != exp_param_types)
return TEE_ERROR_BAD_PARAMETERS;
/* Unused parameters */
(void)¶ms;
(void)&sess_ctx;
IMSG("TEEencrypt Session Opened!\n");
/* If return value != TEE_SUCCESS the session will not be created. */
return TEE_SUCCESS;
}
/*
* Called when a session is closed, sess_ctx hold the value that was
* assigned by TA_OpenSessionEntryPoint().
*/
void TA_CloseSessionEntryPoint(void __maybe_unused *sess_ctx)
{
(void)&sess_ctx; /* Unused parameter */
IMSG("Goodbye!\n");
}
static TEE_Result enc_value(uint32_t param_types,
TEE_Param params[4])
{
// 타입 검사 수행!!!!
uint32_t exp_param_types = TEE_PARAM_TYPES(TEE_PARAM_TYPE_MEMREF_INOUT,
TEE_PARAM_TYPE_VALUE_OUTPUT,
TEE_PARAM_TYPE_NONE,
TEE_PARAM_TYPE_NONE);
char *in = (char *)params[0].memref.buffer;
int len = params[0].memref.size;
int random_key;
DMSG("has been called");
if (param_types != exp_param_types)
return TEE_ERROR_BAD_PARAMETERS;
TEE_GenerateRandom(&random_key, sizeof(random_key));
random_key = (random_key % 25) + 1;
if(random_key < 0) random_key = -random_key;
IMSG("Generated Random Key : %d", random_key);
// 시저 암호화
for(int i=0; i<len; i++){
if(in[i] >= 'a' && in[i] <= 'z'){
in[i] -= 'a';
in[i] += random_key;
in[i] = in[i] % 26;
in[i] += 'a';
}
else if (in[i] >= 'A' && in[i] <= 'Z') {
in[i] -= 'A';
in[i] += random_key;
in[i] = in[i] % 26;
in[i] += 'A';
}
}
IMSG("Ciphertext generated");
params[1].value.a = random_key + ROOT_KEY;
IMSG("Encrypted Random Key sent to CA: %d", params[1].value.a);
return TEE_SUCCESS;
}
static TEE_Result dec_value(uint32_t param_types,
TEE_Param params[4])
{
// 복호화는 나중에...
return TEE_SUCCESS;
}
/*
* Called when a TA is invoked. sess_ctx hold that value that was
* assigned by TA_OpenSessionEntryPoint(). The rest of the paramters
* comes from normal world.
*/
TEE_Result TA_InvokeCommandEntryPoint(void __maybe_unused *sess_ctx,
uint32_t cmd_id,
uint32_t param_types, TEE_Param params[4])
{
(void)&sess_ctx; /* Unused parameter */
switch (cmd_id) {
case TA_TEEencrypt_CMD_ENC_VALUE:
return enc_value(param_types, params);
case TA_TEEencrypt_CMD_DEC_VALUE:
return dec_value(param_types, params);
default:
return TEE_ERROR_BAD_PARAMETERS;
}
}
TEEencrypt_ta.c 파일을 수정하자.
이전에는 단순히 숫자 1을 더하거나 빼는 작업을 수행했고, CA에서는 문자열을 보내는데 TA는 숫자를 받으려고 해서 오류가 발생했다.
랜덤 키 생성과 시저 암호화 로직을 포함한 코드로 수정하자.
TEE_PARAM_TYPES함수에서 파라미터를 모두 검사해준다.
TA는 params[0].memref.buffer에 직접 접근해서 평문을 읽고 암호문을 write..
TEE 내부 API인 TEE_GenerateRandom 를 사용해서 랜덤 키를 생성해준다.
난수를 생성하고 % 25 + 1 연산을 적용해 1~25 사이의 정수로 변환해줌.
CA가 보낸 평문 배열을 순회하면서 random_key 만큼 이동시킨다.
상단에 선언해 둔 ROOT_KEY를 사용해 TA에서 사용할 비밀키를 정의했다.
앞에서 생성한 랜덤 키에 ROOT KEY를 더해서 CA에게 전달한다.
왜? CA에게 랜덤 키를 그대로 주면 위험하니까.. 암호화 작업을 수행해 주는 것.

TA 쪽 코드도 수정했으니 테스트 해 보자.
i -> u (13칸 이동)
3 -> 3 (숫자는 암호화 하지 않는다)
나머지 문자들도 모두 12칸씩 이동함.
TA가 Random Key 12를 생성했고, 시저 암호화를 수행했다.
이제 복호화 기능을 추가하자.
#include <err.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
/* OP-TEE TEE client API (built by optee_client) */
#include <tee_client_api.h>
#include <TEEencrypt_ta.h>
#define MAX_FILE_SIZE 1024
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
TEEC_Result res;
TEEC_Context ctx;
TEEC_Session sess;
TEEC_Operation op;
TEEC_UUID uuid = TA_TEEencrypt_UUID;
uint32_t err_origin;
char plaintext[64] = {0,};
char ciphertext[64] = {0,};
int len = 64;
if(argc < 3) {
printf("Usage:\n");
printf(" Encrypt: %s -e <plaintext_file>\n", argv[0]);
printf(" Decrypt: %s -d <ciphertext_file> <key_file>\n", argv[0]);
return 1;
}
res = TEEC_InitializeContext(NULL, &ctx);
if (res != TEEC_SUCCESS)
errx(1, "TEEC_InitializeContext failed with code 0x%x", res);
res = TEEC_OpenSession(&ctx, &sess, &uuid,
TEEC_LOGIN_PUBLIC, NULL, NULL, &err_origin);
if (res != TEEC_SUCCESS)
errx(1, "TEEC_Opensession failed with code 0x%x origin 0x%x",
res, err_origin);
// 암호화 시작
if(strcmp(argv[1], "-e") == 0) {
printf("========================Encryption========================\n");
FILE *fp = fopen(argv[2], "r");
if(fp == NULL){
printf("File Open Error\n");
return 1;
}
fgets(plaintext, sizeof(plaintext), fp);
fclose(fp);
plaintext[strcspn(plaintext, "\n")] = 0;
len = strlen(plaintext);
printf("Plaintext : %s\n", plaintext);
memset(&op, 0, sizeof(op));
op.paramTypes = TEEC_PARAM_TYPES(TEEC_MEMREF_TEMP_INOUT, TEEC_VALUE_OUTPUT,
TEEC_NONE, TEEC_NONE);
op.params[0].tmpref.buffer = plaintext;
op.params[0].tmpref.size = len;
printf("Invoking TA to encrypt...\n");
res = TEEC_InvokeCommand(&sess, TA_TEEencrypt_CMD_ENC_VALUE, &op,
&err_origin);
if (res != TEEC_SUCCESS)
errx(1, "TEEC_InvokeCommand failed with code 0x%x origin 0x%x",
res, err_origin);
memcpy(ciphertext, op.params[0].tmpref.buffer, len);
printf("Ciphertext : %s\n", ciphertext);
FILE *fp_cipher = fopen("ciphertext.txt", "w");
fputs(ciphertext, fp_cipher);
fclose(fp_cipher);
FILE *fp_key = fopen("encryptedkey.txt", "w");
fprintf(fp_key, "%d", op.params[1].value.a);
fclose(fp_key);
printf("Encryption Complete! Check ciphertext.txt & encryptedkey.txt\n");
}
// 복호화 시작
else if(strcmp(argv[1], "-d") == 0) {
printf("========================Decryption========================\n");
if(argc != 4) {
printf("Usage: %s -d <ciphertext_file> <key_file>\n", argv[0]);
TEEC_CloseSession(&sess);
TEEC_FinalizeContext(&ctx);
return 1;
}
FILE *fp_cipher = fopen(argv[2], "r");
if(fp_cipher == NULL){
printf("Ciphertext File Open Error\n");
return 1;
}
fgets(ciphertext, sizeof(ciphertext), fp_cipher);
fclose(fp_cipher);
ciphertext[strcspn(ciphertext, "\n")] = 0;
len = strlen(ciphertext);
printf("Ciphertext : %s\n", ciphertext);
int encrypted_key = 0;
FILE *fp_key = fopen(argv[3], "r");
if(fp_key == NULL){
printf("Key File Open Error\n");
return 1;
}
fscanf(fp_key, "%d", &encrypted_key);
fclose(fp_key);
printf("Encrypted Key : %d\n", encrypted_key);
memset(&op, 0, sizeof(op));
op.paramTypes = TEEC_PARAM_TYPES(TEEC_MEMREF_TEMP_INOUT, TEEC_VALUE_INPUT,
TEEC_NONE, TEEC_NONE);
op.params[0].tmpref.buffer = ciphertext;
op.params[0].tmpref.size = len;
op.params[1].value.a = encrypted_key;
printf("Invoking TA to decrypt...\n");
res = TEEC_InvokeCommand(&sess, TA_TEEencrypt_CMD_DEC_VALUE, &op,
&err_origin);
if (res != TEEC_SUCCESS)
errx(1, "TEEC_InvokeCommand failed with code 0x%x origin 0x%x",
res, err_origin);
memcpy(plaintext, op.params[0].tmpref.buffer, len);
printf("Plaintext : %s\n", plaintext);
FILE *fp_plain = fopen("plaintext.txt", "w");
fputs(plaintext, fp_plain);
fclose(fp_plain);
printf("Decryption Complete! Check plaintext.txt\n");
}
TEEC_CloseSession(&sess);
TEEC_FinalizeContext(&ctx);
return 0;
}
우선 host의 main.c 부터 작업하자.
초기화 -> 암호화 -> 복호화 단계로 구성된다.
이전과의 차이는 -d 옵션으로 복호화하는 로직이 추가됐다는 점.
-d 옵션을 입력하면 복호화 로직을 수행한다.
이 때 암호문과 암호화된 키가 필요함. 각각 argv[2]와 argv[3]에서 fscanf로 가져온다.
암호화 할 때는 param[1]을 TEEC_VALUE_OUTPUT으로 사용하고, 복호화 할 때는 param[1]을 TEEC_VALUE_INPUT으로 사용한다.
저거에 맞춰서 호출하는 TA 명령어도 다름. TA_TEEencrypt_CMD_ENC_VALUE / TA_TEEencrypt_CMD_DEC_VALUE
#include <tee_internal_api.h>
#include <tee_internal_api_extensions.h>
#include <TEEencrypt_ta.h>
#define ROOT_KEY 3
/*
* Called when the instance of the TA is created.
*/
TEE_Result TA_CreateEntryPoint(void)
{
DMSG("has been called");
return TEE_SUCCESS;
}
/*
* Called when the instance of the TA is destroyed.
*/
void TA_DestroyEntryPoint(void)
{
DMSG("has been called");
}
/*
* Called when a new session is opened to the TA.
*/
TEE_Result TA_OpenSessionEntryPoint(uint32_t param_types,
TEE_Param __maybe_unused params[4],
void __maybe_unused **sess_ctx)
{
uint32_t exp_param_types = TEE_PARAM_TYPES(TEE_PARAM_TYPE_NONE,
TEE_PARAM_TYPE_NONE,
TEE_PARAM_TYPE_NONE,
TEE_PARAM_TYPE_NONE);
DMSG("has been called");
if (param_types != exp_param_types)
return TEE_ERROR_BAD_PARAMETERS;
(void)¶ms;
(void)&sess_ctx;
IMSG("TEEencrypt Session Opened!\n");
return TEE_SUCCESS;
}
/*
* Called when a session is closed.
*/
void TA_CloseSessionEntryPoint(void __maybe_unused *sess_ctx)
{
(void)&sess_ctx;
IMSG("Goodbye!\n");
}
static TEE_Result enc_value(uint32_t param_types,
TEE_Param params[4])
{
uint32_t exp_param_types = TEE_PARAM_TYPES(TEE_PARAM_TYPE_MEMREF_INOUT,
TEE_PARAM_TYPE_VALUE_OUTPUT,
TEE_PARAM_TYPE_NONE,
TEE_PARAM_TYPE_NONE);
char *in = (char *)params[0].memref.buffer;
int len = params[0].memref.size;
int random_key;
DMSG("has been called");
if (param_types != exp_param_types)
return TEE_ERROR_BAD_PARAMETERS;
TEE_GenerateRandom(&random_key, sizeof(random_key));
random_key = (random_key % 25) + 1;
if(random_key < 0) random_key = -random_key;
IMSG("Generated Random Key : %d", random_key);
// 시저 암호화
for(int i=0; i<len; i++){
if(in[i] >= 'a' && in[i] <= 'z'){
in[i] -= 'a';
in[i] += random_key;
in[i] = in[i] % 26;
in[i] += 'a';
}
else if (in[i] >= 'A' && in[i] <= 'Z') {
in[i] -= 'A';
in[i] += random_key;
in[i] = in[i] % 26;
in[i] += 'A';
}
}
IMSG("Ciphertext generated");
params[1].value.a = random_key + ROOT_KEY;
IMSG("Encrypted Random Key sent to CA: %d", params[1].value.a);
return TEE_SUCCESS;
}
// 복호화
static TEE_Result dec_value(uint32_t param_types,
TEE_Param params[4])
{
uint32_t exp_param_types = TEE_PARAM_TYPES(TEE_PARAM_TYPE_MEMREF_INOUT,
TEE_PARAM_TYPE_VALUE_INPUT,
TEE_PARAM_TYPE_NONE,
TEE_PARAM_TYPE_NONE);
char *in = (char *)params[0].memref.buffer;
int len = params[0].memref.size;
int encrypted_key = params[1].value.a;
int random_key;
DMSG("has been called");
if (param_types != exp_param_types)
return TEE_ERROR_BAD_PARAMETERS;
random_key = encrypted_key - ROOT_KEY;
IMSG("Restored Random Key : %d", random_key);
for(int i=0; i<len; i++){
if(in[i] >= 'a' && in[i] <= 'z'){
in[i] -= 'a';
in[i] -= random_key;
in[i] += 26;
in[i] = in[i] % 26;
in[i] += 'a';
}
else if (in[i] >= 'A' && in[i] <= 'Z') {
in[i] -= 'A';
in[i] -= random_key;
in[i] += 26;
in[i] = in[i] % 26;
in[i] += 'A';
}
}
IMSG("Plaintext restored");
return TEE_SUCCESS;
}
TEE_Result TA_InvokeCommandEntryPoint(void __maybe_unused *sess_ctx,
uint32_t cmd_id,
uint32_t param_types, TEE_Param params[4])
{
(void)&sess_ctx;
switch (cmd_id) {
case TA_TEEencrypt_CMD_ENC_VALUE:
return enc_value(param_types, params);
case TA_TEEencrypt_CMD_DEC_VALUE:
return dec_value(param_types, params);
default:
return TEE_ERROR_BAD_PARAMETERS;
}
}
dec_value 함수를 구현했다.
복호화 할 때는 CA가 파일에서 읽은 암호화된 키를 TA에게 전달해야 하니 params[1]의 타입이 INPUT으로 변경됐다.
암호화 할 때는 ROOT_KEY를 더했으니, 복호화 할 때는 ROOT_KEY를 빼 준다.
시저 암호 복호화니까 왼쪽으로 Shift 해준다.
음수가 될 수 있으니.. 이 부분을 방지하기 위해 +26을 더하고 %26으로 사이클을 유지해줌.


다시 빌드하고 최종 테스트 해 보자.
우선 encrypt 해서 ciphertext랑 encryptedkey를 얻음.

-d 옵션으로 복호화까지 테스트했다.
이제 RSA 암호화를 구현해보자.

우선 헤더파일에 TA_TEEencrypt_CMD_RSA_ENC_VALUE 값을 추가해줬다.
#include <tee_internal_api.h>
#include <tee_internal_api_extensions.h>
#include <TEEencrypt_ta.h>
#define ROOT_KEY 3
#define RSA_KEY_SIZE 1024
#define MAX_PLAIN_LEN_1024 86
/*
* Called when the instance of the TA is created.
*/
TEE_Result TA_CreateEntryPoint(void)
{
DMSG("has been called");
return TEE_SUCCESS;
}
/*
* Called when the instance of the TA is destroyed.
*/
void TA_DestroyEntryPoint(void)
{
DMSG("has been called");
}
/*
* Called when a new session is opened to the TA.
*/
TEE_Result TA_OpenSessionEntryPoint(uint32_t param_types,
TEE_Param __maybe_unused params[4],
void __maybe_unused **sess_ctx)
{
uint32_t exp_param_types = TEE_PARAM_TYPES(TEE_PARAM_TYPE_NONE,
TEE_PARAM_TYPE_NONE,
TEE_PARAM_TYPE_NONE,
TEE_PARAM_TYPE_NONE);
DMSG("has been called");
if (param_types != exp_param_types)
return TEE_ERROR_BAD_PARAMETERS;
(void)¶ms;
(void)&sess_ctx;
IMSG("TEEencrypt Session Opened!\n");
return TEE_SUCCESS;
}
/*
* Called when a session is closed.
*/
void TA_CloseSessionEntryPoint(void __maybe_unused *sess_ctx)
{
(void)&sess_ctx;
IMSG("Goodbye!\n");
}
// 시저 암호화
static TEE_Result enc_value(uint32_t param_types,
TEE_Param params[4])
{
uint32_t exp_param_types = TEE_PARAM_TYPES(TEE_PARAM_TYPE_MEMREF_INOUT,
TEE_PARAM_TYPE_VALUE_OUTPUT,
TEE_PARAM_TYPE_NONE,
TEE_PARAM_TYPE_NONE);
char *in = (char *)params[0].memref.buffer;
int len = params[0].memref.size;
int random_key;
DMSG("has been called");
if (param_types != exp_param_types)
return TEE_ERROR_BAD_PARAMETERS;
TEE_GenerateRandom(&random_key, sizeof(random_key));
random_key = (random_key % 25) + 1;
if(random_key < 0) random_key = -random_key;
IMSG("Generated Random Key : %d", random_key);
for(int i=0; i<len; i++){
if(in[i] >= 'a' && in[i] <= 'z'){
in[i] -= 'a';
in[i] += random_key;
in[i] = in[i] % 26;
in[i] += 'a';
}
else if (in[i] >= 'A' && in[i] <= 'Z') {
in[i] -= 'A';
in[i] += random_key;
in[i] = in[i] % 26;
in[i] += 'A';
}
}
IMSG("Ciphertext generated");
params[1].value.a = random_key + ROOT_KEY;
IMSG("Encrypted Random Key sent to CA: %d", params[1].value.a);
return TEE_SUCCESS;
}
// 복호화
static TEE_Result dec_value(uint32_t param_types,
TEE_Param params[4])
{
uint32_t exp_param_types = TEE_PARAM_TYPES(TEE_PARAM_TYPE_MEMREF_INOUT,
TEE_PARAM_TYPE_VALUE_INPUT,
TEE_PARAM_TYPE_NONE,
TEE_PARAM_TYPE_NONE);
char *in = (char *)params[0].memref.buffer;
int len = params[0].memref.size;
int encrypted_key = params[1].value.a;
int random_key;
DMSG("has been called");
if (param_types != exp_param_types)
return TEE_ERROR_BAD_PARAMETERS;
random_key = encrypted_key - ROOT_KEY;
IMSG("Restored Random Key : %d", random_key);
for(int i=0; i<len; i++){
if(in[i] >= 'a' && in[i] <= 'z'){
in[i] -= 'a';
in[i] -= random_key;
in[i] += 26;
in[i] = in[i] % 26;
in[i] += 'a';
}
else if (in[i] >= 'A' && in[i] <= 'Z') {
in[i] -= 'A';
in[i] -= random_key;
in[i] += 26;
in[i] = in[i] % 26;
in[i] += 'A';
}
}
IMSG("Plaintext restored");
return TEE_SUCCESS;
}
// RSA 암호화
static TEE_Result rsa_encrypt(uint32_t param_types, TEE_Param params[4]) {
TEE_Result res;
TEE_ObjectHandle key_pair = TEE_HANDLE_NULL;
TEE_OperationHandle operation = TEE_HANDLE_NULL;
uint32_t rsa_alg = TEE_ALG_RSAES_PKCS1_V1_5;
uint32_t exp_param_types = TEE_PARAM_TYPES(TEE_PARAM_TYPE_MEMREF_INPUT,
TEE_PARAM_TYPE_MEMREF_OUTPUT,
TEE_PARAM_TYPE_NONE,
TEE_PARAM_TYPE_NONE);
if (param_types != exp_param_types)
return TEE_ERROR_BAD_PARAMETERS;
void *in_buf = params[0].memref.buffer;
size_t in_len = params[0].memref.size;
void *out_buf = params[1].memref.buffer;
size_t out_len = params[1].memref.size;
res = TEE_AllocateTransientObject(TEE_TYPE_RSA_KEYPAIR, RSA_KEY_SIZE, &key_pair);
if (res != TEE_SUCCESS) {
EMSG("Failed to allocate transient object handle: 0x%x", res);
return res;
}
res = TEE_GenerateKey(key_pair, RSA_KEY_SIZE, NULL, 0);
if (res != TEE_SUCCESS) {
EMSG("Failed to generate key: 0x%x", res);
goto err;
}
res = TEE_AllocateOperation(&operation, rsa_alg, TEE_MODE_ENCRYPT, RSA_KEY_SIZE);
if (res != TEE_SUCCESS) {
EMSG("Failed to allocate operation: 0x%x", res);
goto err;
}
res = TEE_SetOperationKey(operation, key_pair);
if (res != TEE_SUCCESS) {
EMSG("Failed to set operation key: 0x%x", res);
goto err;
}
res = TEE_AsymmetricEncrypt(operation, NULL, NULL, 0, in_buf, in_len, out_buf, &out_len);
if (res != TEE_SUCCESS) {
EMSG("RSA Encryption failed: 0x%x", res);
goto err;
}
params[1].memref.size = out_len;
IMSG("RSA Encryption Complete. Ciphertext size: %d", (int)out_len);
err:
if (operation != TEE_HANDLE_NULL)
TEE_FreeOperation(operation);
if (key_pair != TEE_HANDLE_NULL)
TEE_FreeTransientObject(key_pair);
return res;
}
TEE_Result TA_InvokeCommandEntryPoint(void __maybe_unused *sess_ctx,
uint32_t cmd_id,
uint32_t param_types, TEE_Param params[4])
{
(void)&sess_ctx;
switch (cmd_id) {
case TA_TEEencrypt_CMD_ENC_VALUE:
return enc_value(param_types, params);
case TA_TEEencrypt_CMD_DEC_VALUE:
return dec_value(param_types, params);
case TA_TEEencrypt_CMD_RSA_ENC_VALUE:
return rsa_encrypt(param_types, params);
default:
return TEE_ERROR_BAD_PARAMETERS;
}
}
이 다음은 실제 구현 부분.
RSA 알고리즘을 사용하기 위한 필요한 키 크기와 버퍼 크기를 정의해준다.
rsa_encrypt 함수를 새로 작성함.
1. Key 객체 할당 - TEE_AllocateTransientObject로 메모리 할당, TEE_GenerateKey로 RSA 공개키와 개인키 생성
2. 암호화 연산 관련 설정 - TEE_ALG_RSAES_PKCS1_V1_5 RSA 알고리즘을 사용하는 연산을 생성
3. 암호화 - 평문을 암호화해 출력 버퍼에 저장
https://github.com/cezane/optee_rsa_example 여기에 있는 핵심 코드를 가져와서 프로젝트에 적용함.
키 할당 / 생성 / 암호화 로직만 뽑아와서 rsa_encrypt 함수 작성에 사용했다.
#include <err.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
/* OP-TEE TEE client API (built by optee_client) */
#include <tee_client_api.h>
#include <TEEencrypt_ta.h>
#define RSA_KEY_SIZE 1024
#define MAX_FILE_SIZE 1024
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
TEEC_Result res;
TEEC_Context ctx;
TEEC_Session sess;
TEEC_Operation op;
TEEC_UUID uuid = TA_TEEencrypt_UUID;
uint32_t err_origin;
char plaintext[1024] = {0,};
char ciphertext[1024] = {0,};
int len = 1024;
if(argc < 3) {
printf("Usage:\n");
printf(" Encrypt (Caesar): %s -e <file>\n", argv[0]);
printf(" Encrypt (RSA) : %s -e <file> RSA\n", argv[0]);
printf(" Decrypt (Caesar): %s -d <file> <key>\n", argv[0]);
return 1;
}
res = TEEC_InitializeContext(NULL, &ctx);
if (res != TEEC_SUCCESS)
errx(1, "TEEC_InitializeContext failed with code 0x%x", res);
res = TEEC_OpenSession(&ctx, &sess, &uuid,
TEEC_LOGIN_PUBLIC, NULL, NULL, &err_origin);
if (res != TEEC_SUCCESS)
errx(1, "TEEC_Opensession failed with code 0x%x origin 0x%x",
res, err_origin);
if(strcmp(argv[1], "-e") == 0) {
printf("========================Encryption========================\n");
FILE *fp = fopen(argv[2], "r");
if(fp == NULL){
printf("File Open Error\n");
return 1;
}
fgets(plaintext, sizeof(plaintext), fp);
fclose(fp);
plaintext[strcspn(plaintext, "\n")] = 0;
len = strlen(plaintext);
printf("Plaintext : %s\n", plaintext);
if (argc == 4 && strcmp(argv[3], "RSA") == 0) {
printf("Mode: RSA Encryption\n");
memset(&op, 0, sizeof(op));
op.paramTypes = TEEC_PARAM_TYPES(TEEC_MEMREF_TEMP_INPUT,
TEEC_MEMREF_TEMP_OUTPUT,
TEEC_NONE, TEEC_NONE);
op.params[0].tmpref.buffer = plaintext;
op.params[0].tmpref.size = len;
op.params[1].tmpref.buffer = ciphertext;
op.params[1].tmpref.size = RSA_KEY_SIZE / 8;
printf("Invoking TA to encrypt with RSA...\n");
res = TEEC_InvokeCommand(&sess, TA_TEEencrypt_CMD_RSA_ENC_VALUE, &op, &err_origin);
if (res != TEEC_SUCCESS)
errx(1, "RSA InvokeCommand failed 0x%x origin 0x%x", res, err_origin);
int cipher_len = op.params[1].tmpref.size;
printf("Ciphertext generated (Len: %d)\n", cipher_len);
FILE *fp_cipher = fopen("ciphertext_rsa.txt", "w");
fwrite(ciphertext, 1, cipher_len, fp_cipher);
fclose(fp_cipher);
printf("RSA Encryption Complete! Check ciphertext_rsa.txt\n");
} else {
printf("Mode: Caesar Encryption\n");
memset(&op, 0, sizeof(op));
op.paramTypes = TEEC_PARAM_TYPES(TEEC_MEMREF_TEMP_INOUT, TEEC_VALUE_OUTPUT,
TEEC_NONE, TEEC_NONE);
op.params[0].tmpref.buffer = plaintext;
op.params[0].tmpref.size = len;
printf("Invoking TA to encrypt with Caesar...\n");
res = TEEC_InvokeCommand(&sess, TA_TEEencrypt_CMD_ENC_VALUE, &op,
&err_origin);
if (res != TEEC_SUCCESS)
errx(1, "TEEC_InvokeCommand failed with code 0x%x origin 0x%x",
res, err_origin);
memcpy(ciphertext, op.params[0].tmpref.buffer, len);
printf("Ciphertext : %s\n", ciphertext);
FILE *fp_cipher = fopen("ciphertext.txt", "w");
fputs(ciphertext, fp_cipher);
fclose(fp_cipher);
FILE *fp_key = fopen("encryptedkey.txt", "w");
fprintf(fp_key, "%d", op.params[1].value.a);
fclose(fp_key);
printf("Caesar Encryption Complete! Check ciphertext.txt & encryptedkey.txt\n");
}
}
else if(strcmp(argv[1], "-d") == 0) {
printf("========================Decryption========================\n");
if(argc != 4) {
printf("Usage: %s -d <ciphertext_file> <key_file>\n", argv[0]);
TEEC_CloseSession(&sess);
TEEC_FinalizeContext(&ctx);
return 1;
}
FILE *fp_cipher = fopen(argv[2], "r");
if(fp_cipher == NULL){
printf("Ciphertext File Open Error\n");
return 1;
}
fgets(ciphertext, sizeof(ciphertext), fp_cipher);
fclose(fp_cipher);
ciphertext[strcspn(ciphertext, "\n")] = 0;
len = strlen(ciphertext);
printf("Ciphertext : %s\n", ciphertext);
int encrypted_key = 0;
FILE *fp_key = fopen(argv[3], "r");
if(fp_key == NULL){
printf("Key File Open Error\n");
return 1;
}
fscanf(fp_key, "%d", &encrypted_key);
fclose(fp_key);
printf("Encrypted Key : %d\n", encrypted_key);
memset(&op, 0, sizeof(op));
op.paramTypes = TEEC_PARAM_TYPES(TEEC_MEMREF_TEMP_INOUT, TEEC_VALUE_INPUT,
TEEC_NONE, TEEC_NONE);
op.params[0].tmpref.buffer = ciphertext;
op.params[0].tmpref.size = len;
op.params[1].value.a = encrypted_key;
printf("Invoking TA to decrypt...\n");
res = TEEC_InvokeCommand(&sess, TA_TEEencrypt_CMD_DEC_VALUE, &op,
&err_origin);
if (res != TEEC_SUCCESS)
errx(1, "TEEC_InvokeCommand failed with code 0x%x origin 0x%x",
res, err_origin);
memcpy(plaintext, op.params[0].tmpref.buffer, len);
printf("Plaintext : %s\n", plaintext);
FILE *fp_plain = fopen("plaintext.txt", "w");
fputs(plaintext, fp_plain);
fclose(fp_plain);
printf("Decryption Complete! Check plaintext.txt\n");
}
TEEC_CloseSession(&sess);
TEEC_FinalizeContext(&ctx);
return 0;
}
기존에는 -e와 -d 옵션만 처리할 수 있었으니 RSA 암호화도 사용할 수 있도록 -e ... RSA 도 추가해주자.
이 때 크기를 1024로 설정해줘야 함.. 안그러면 Segmentation Fault 뜬다.
RSA에서는 파라미터 타입이 기존과 다르다. TEEC_MEMREF_TEMP_INPUT + TEEC_MEMREF_TEMP_OUTPUT
평문보다 길어질 수 있으니 입력 버퍼와 출력 버퍼를 분리한다.
TA_TEEencrypt_CMD_RSA_ENC_VALUE 를 사용해서 TA 에게 RSA 함수를 요청한다.
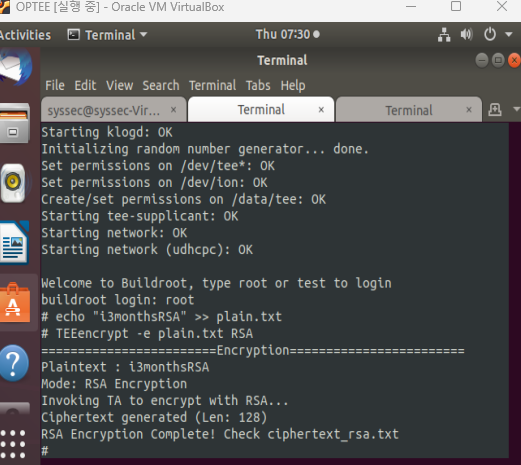

다시 빌드하고 실행하면 RSA 도 제대로 동작함. RSA 복호화는 패스..
개인키를 TEE 내부에 안전하게 보관하고, TA 안에서 처리한다.
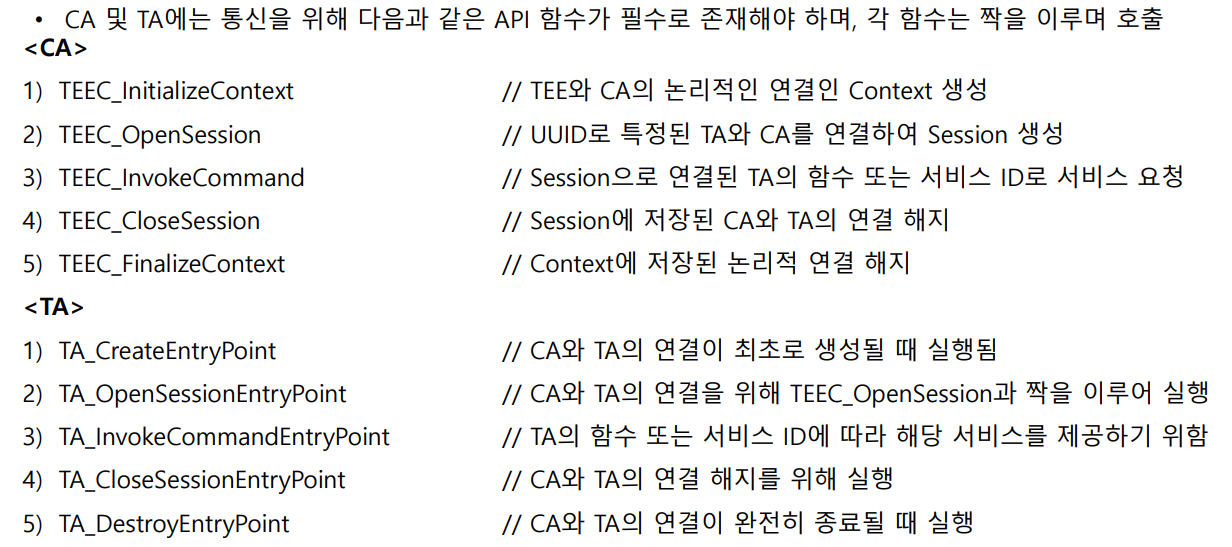
아래는 참고..

'Computer Science > Computer Security' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [SSS] Hardware-based Security Techniques (0) | 2025.11.27 |
|---|---|
| [SSS] Trusted Execution Environment 2 (0) | 2025.11.24 |
| [SSS] Trusted Execution Environment (0) | 2025.11.14 |
| [SSS] Software Defense (0) | 2025.11.10 |
| [SSS] OS kernel and Rootkit (0) | 2025.11.01 |
댓글
이 글 공유하기
다른 글
-
[SSS] Hardware-based Security Techniques
[SSS] Hardware-based Security Techniques
2025.11.27 -
[SSS] Trusted Execution Environment 2
[SSS] Trusted Execution Environment 2
2025.11.24 -
[SSS] Trusted Execution Environment
[SSS] Trusted Execution Environment
2025.11.14 -
[SSS] Software Defense
[SSS] Software Defense
2025.11.10